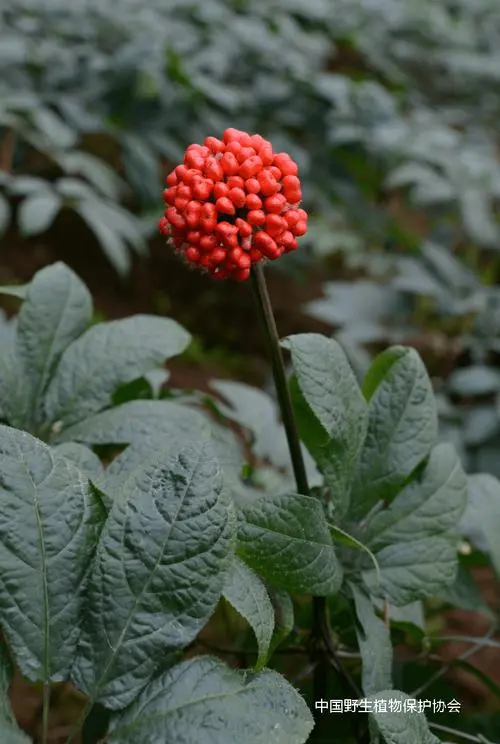
Sanqi, also known as Panax notoginseng or Tianqi in Chinese, is a highly revered medicinal herb native to the Yunnan Province of China. With a rich history dating back thousands of years, this plant has been an integral part of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) due to its remarkable therapeutic properties.
**Botanical Profile**
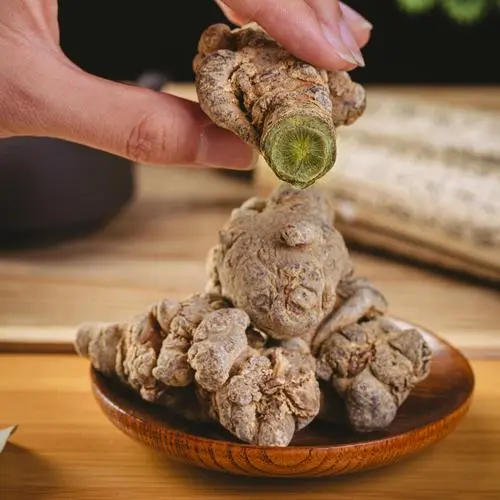

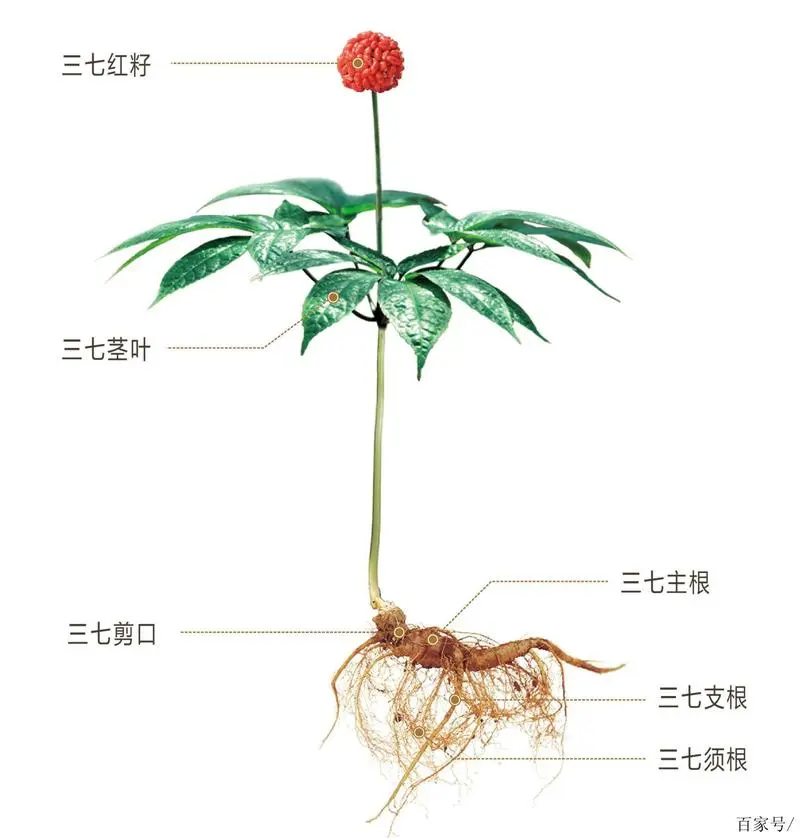
Sanqi belongs to the Araliaceae family and is closely related to other well-known ginseng species such as American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) and Asian ginseng (Panax ginseng). The plant typically grows in the wild under semi-shaded and moist environments, with its most valuable part being the root, which exhibits a reddish-brown hue and a characteristic forked shape, hence earning it the nickname “three-seven” because of the typical three-pronged growth pattern at the root tip.
**Medicinal Properties**
In TCM, Sanqi is considered a yang tonic that nourishes blood, stops bleeding, dissipates blood stasis, and promotes tissue repair. It contains a variety of bioactive compounds, notably ginsenosides, notoginsenosides, flavonoids, and polysaccharides, which contribute to its pharmacological activities. These compounds are believed to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticoagulant, and cardiovascular protective effects.
**Traditional Uses**

Traditionally, Sanqi is used to treat a wide range of health conditions, including traumatic injuries, internal and external bleeding, bruises, pain management, and menstrual disorders. It is often applied topically for wound healing and taken internally as a decoction, powder, or extract to help improve blood circulation and alleviate symptoms associated with various circulatory problems.

**Modern Applications**
In contemporary medicine, Panax notoginseng has gained scientific recognition for its potential benefits. Research indicates its effectiveness in managing cardiovascular diseases by reducing blood pressure, preventing thrombosis, and improving microcirculation. Additionally, studies suggest it may have applications in neuroprotection, diabetes treatment, and as a supportive therapy during recovery from surgery.
**Preparation and Dosage**
The preparation method of Sanqi varies depending on the intended use. It can be consumed as a dried powdered herb mixed into capsules, brewed as a tea, or processed into extracts or tinctures. For safety and efficacy, it’s crucial to follow professional advice regarding dosage and usage, as self-administration could lead to unwanted side effects if not properly regulated.
In conclusion, Sanqi holds a significant place in both ancient and modern healthcare systems due to its potent health benefits. Its unique blend of tradition and science continues to attract researchers worldwide, leading to further exploration of its therapeutic potential and expanded applications within global medical practices. As with any herbal remedy, it is essential to consult a licensed practitioner before incorporating Sanqi into your healthcare regimen.
